Specifications container
Standard Dry Cargo Container
- specifications

Open Top Container
- specifications

Flat Rack Container
- specifications

Refrigerated Container
- specifications

Incoterms
The rules have been developed and maintained by experts and practitioners brought together by ICC and have become the standard in international business rules setting. Launched in mid-September 2010, Incoterms® 2010 came into effect on 1 January 2011. They help traders avoid costly misunderstandings by clarifying the tasks, costs and risks involved in the delivery of goods from sellers to buyers. Incoterms® rules are recognized by UNCITRAL as the global standard for the interpretation of the most common terms in foreign trade.
Please note that all contracts made under INCOTERMS® 2000 remain valid even after 2011. Moreover, although we recommend using Incoterms® 2010 after 2011, parties to a contract for the sale of goods can agree to choose any version of the Incoterms rules after 2011. It is important however to clearly specify the chosen version INCOTERMS® 2010, INCOTERMS® 2000 or any earlier version.
• Spreadsheet Incoterms
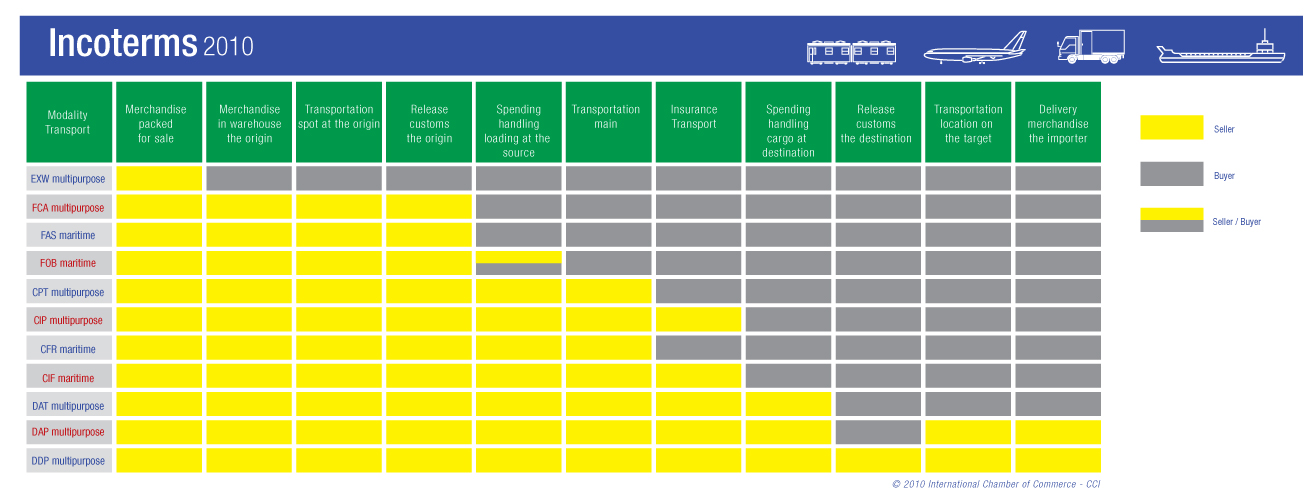
• EXW - Ex Works (Named Places of Delivery)
Ex Works” means that the seller delivers when it places the goods at the disposal of the buyer at the seller’s premises or at another named place (i.e.,works, factory, warehouse, etc.).
The seller does not need to load the goods on any collecting vehicle, nor does it need to clear the goods for export, where such clearance is applicable.
• FCA - Free Carrier (named place of delivery)
Free Carrier” means that the seller delivers the goods to the carrier or another person nominated by the buyer at the seller’s premises or another named place.
The parties are well advised to specify as clearly as possible the point within the named place of delivery, as the risk passes to the buyer at that point.
• CPT - Carriage Paid To (named place of destination)
Carriage Paid To” means that the seller delivers the goods to the carrier or another person nominated by the seller at an agreed place (if any such place is agreed between parties) and that the seller must contract for and pay the costs of carriage necessary to bring the goods to the named place of destination.
• CIP - Carriage and Insurance Paid to (named pplace of destination)
Carriage and Insurance Paid to” means that the seller delivers the goods to the carrier or another person nominated by the seller at an agreed place (if any such place is agreed between parties) and that the seller must contract for an pay the costs of carriage necessary to bring the goods to the named place of destination.
The seller also contracts for insurance cover against the buyer’s risk of loss of or damage to the goods during the carriage. The buyer should note that under CIP the seller is required to obtain insurance only on minimum cover. Should the buyer wish to have more insurance protection, it will need either to agree as much expressly with the seller or to make its own extra insurance arrangements.
• DAT - Delivered At Terminal (named terminal at port or place of destination)
Delivered at Terminal” means that the seller delivers when the goods, once unloaded from the arriving means of transport, are placed at the disposal of the buyer at a named terminal at the named port or place of destination.
“Terminal” includes a place, whether covered or not, such as a quay, warehouse, container yard or road, rail or air cargo terminal.
The seller bears all risks involved in bringing the goods to and unloading them at the terminal at the named port or place of destination.
• DAP - Delivered At Place (named place of destination)
Delivered at Place” means that the seller delivers when the goods are placed at the disposal of the buyer on the arriving means of transport ready for unloading at the named place of destination.
The seller bears all risks involved in bringing the goods to the named place.
• DDP - Delivered Duty Paid (named place of destination)
Delivered Duty Paid” means that the seller delivers the goods when the goods are placed at the disposal of the buyer, cleared for import on the arriving means of transport ready for unloading at the named place of destination.
The seller bears all the costs and risks involved in bringing the goods to the place of destination and has an obligation to clear the goods not only for export but also for import, to pay any duty for both export and import and to carry out all customs formalities.
• FAS - Free Alongside Ship (named port of shipment)
Free Alongside Ship” means that the seller delivers when the goods are placed alongside the vessel (e.g., on a quay or a barge) nominated by the buyer at the named port of shipment.
The risk of loss of or damage to the goods passes when the goods are alongside the ship, and the buyer bears all costs from that moment onwards.
• FOB - Free On Board (named port of shipment)
Free On Board” means that the seller delivers the goods on board the vessel nominated by the buyer at the named port of shipment or procures the goods already so delivered.
The risk of loss of or damage to the goods passes when the goods are on board the vessel, and the buyer bears all costs from that moment onwards.
• CFR costa and Freight (named port of destination)
Cost and Freight” means that the seller delivers the goods on board the vessel or procures the goods already so delivered.
The risk of loss of or damage to the goods passes when the goods are on board the vessel. the seller must contract for and pay the costs and freight necessary to bring the goods to the named port of destination.
• CIF - Cost, Insurance and Freight (named por of destination)
Cost, Insurance and Freight” means that the seller delivers the goods on board the vessel or procures the goods already so delivered. The risk of loss of or damage to the goods passes when the goods are on board the vessel.
The seller must contract for and pay the costs and freight necessary to bring the goods to the named port of destination.
Dictionary of foreign trade and logistics
• Letter A
• AA - Always Afloat
• AAAA - Always Accessible Always Afloat
• AARA - Amsterdam-Antwerp-Rotterdam Area
• ABT - About
• ADCOM - Address Commission
• AFSPS - Arrival First Sea Pilot Station (Norway)
• AFFREIGHTMENT - The hiring of a ship in whole or part
• AFT - At or towards the stern or rear of a ship
• AGW - All Going Well
• AHL - Australian Hold Ladders
• ANTHAM - Antwerp-Hamburg Range
• APS - Arrival Pilot Station
• ARAG - Amsterdam-Rotterdam--Antwerp-Ghent Range
• A/S - Alongside
• ATDNSHINC - Any Time Day or Night Sundays and Holidays Included
• ATUTC - Actual Times Used to Count
• Letter B
• BAF - Bunker Adjustment Factor. A Fuel Surcharge expressed as percentage added or subtracted from the freight amount reflecting the movement in the market place price for bunkers.
• BALLAST - Heavy weight, often sea water, necessary for the stability and safety of a ship which is not carying cargo.
• BAREBOAT CHTR - Bareboat Charter - Owners lease a specific ship and control its technical management and commercial operations only.
• BBB - Before Breaking Bulk
• BDI - Both Dates Inclusive
• BENDS - Both Ends (Load & Discharge Ports)
• BI - Both Inclusive
• BIMCO - The Baltic and International Maritime Council
• BL (1) - Bale
• BL (2) - (Bill of Lading) A document signed by the carrier which acts as a receipt and evidence of title to the cargo.
• BM - Beam
• BEAM - The maximum breadth of a ship
• BOB - Bunker on Board
• BOFFER - Best Offer
• BROB - Bunkers Remaining on Board
• BSS - Basis
• BSS 1/1 - Basis 1 Port to 1 Port
• BT - Berth Terms
• BUNDLING - This is the assembly of pieces of cargo, secured into one manageable unit. This is a very flexible description, a rule of thumb is to present cargo at a size easily handled by a large (20 tonne) fork lift truck.
• BUNKERS - Name given for vessels Fuel and Diesel Oil supplies (Originates from coal bunkers)
• BWAD - Brackish Water Arrival Draft
• Letter C
• CBM - Cubic Meter
• CBFT (or CFT) - Cubic Feet
• CFR (or C&F) - Cost and Freight
• CHOPT - Charterers Option
• CHTRS - Charterers
• CIF - Cost, Insurance & Freight. Seller pays all these costs to a nominated port or place of discharge.
• COA - Contract of Affreightment - Owners agree to accept a cost per revenue ton for cargo carried on a specific number of voyages.
• COACP - Contract of Affreightment Charter Party
• COB - Close of Business
• COD - Cash On Delivery
• COGSA - Carriage of Goods by Sea Act
• CONS - Consumption
• COP - Custom Of Port
• CP (or C/P) - Charter Party
• CPD - Charterers Pay Dues
• CPT - Carriage Paid To
• CQD - Customary Quick Despatch
• CROB - Cargo Remaining on Board
• CRN - Crane
• CST - Centistoke
• CTR - Container Fitted
• CVE - Communication / Victuals / Entertainment
• Letter D
• DAPS - Days all Purposes (Total days for loading & discharging)
• DDU - Delivered Duty unpaid.
• DDP - Delivered Duty Paid.
• DEM - Demurrage
• DESP - Despatch
• DET - Detention
• DHDATSBE - Despatch Half Demurrage on Actual Time Saved Both Ends
• DHDWTSBE - Despatch Half Demurrage on Working Time Saved Both Ends
• DISCH - Discharge
• DK - Deck
• DLOSP - Dropping Last Outwards Sea Pilot (Norway)
• DO - Dropping Off Last Sea Pilot (Norway)
• DOP - Dropping Outward Pilot
• DOT - Department of Transport
• DNRSAOCLONL - Discountless and Non-Returnable Ship and/or Cargo Lost or Not Lost
• DRAFT - Depth to which a ship is immersed in water. The depth varies according to the design of the ship and will be greater or lesser depending not only on the weight of the ship and everything on board, but also on the density of the water in which the ship is lying.
• DRK - Derrick
• DUNNAGE - Materials of various types, often timber or matting, placed among the cargo for separation, and hence protection from damage, for ventilation and, in the case of certain cargoes, to provide space in which the forks of a lift truck may be inserted.
• DWAT (or DWT) - Deadweight. Weight of cargo, stores and water, i.e. the difference between lightship and loaded displacement.
• Letter E
• EC - East Coast
• EIU - Even if Used
• ELVENT - Electric Ventilation
• ETA - Estimated Time of Arrival
• ETC - Estimated Time of Completion
• ETD - Estimated Time of Departure
• ETS - Estimated Time of Sailing
• EXW - Ex Works
• Letter F
• FAS - Free Alongside Ship. Seller delivers goods to appropriate dock or terminal at port of embarkation and buyer covers costs and risks of loading.
• FD - Free of Despatch
• FDD - Freight Demurrage Deadfreight
• FDIS - Free Discharge
• FEU - Forty foot container equivalency unit - Standard 40‘Container
• FHEX - Fridays/Holidays Excluded
• FHINC - Fridays/Holidays Included
• FILO - Free In/Liner Out. Seafreight with which the shipper pays load costs and the carrier pays for discharge Free In/Out. Freight booked FIO includes the seafreight, but no loading/discharging costs, i.e. the charterer pays for cost of loading and discharging cargo.
• FIOS - Free In/Out Stowed. As per FIO, but includes stowage costs.
• FIOT - Free In/Out and Trimmed. As per FIOS but includes trimming - the leveling of bulk cargoes
• FIOSLSD - Free In/Out Stowed, Lashed, Secured and Dunnaged. As per FIO, but includes cost of lashing securing and dunnaging cargo to Masters satisfaction.
• FIOST - Free In/Out and Trimmed. Charterer pays for cost of loading/discharging cargo, including stowage and trimming.
• FIT - Free In Trimmed
• FIW - Free In Wagon
• FIXING - Chartering a Vessel
• FLT - Full Liner Terms - Shipowner pays to load and discharge the cargo
• FMC - Federal Maritime Commission - US government agency
• FMS - Fathoms - 6 feet
• FO (IFO) - Fuel Oil/Intermediate FO
• FOB - Free on Board. Seller sees the goods „over the ship‘s rail“ on to the ship which is arranged and paid for by the buyer
• FOFFER - Firm Offer
• FOG - For Our Guidance
• FOQ - Free On Quay
• FOR - Free On Rail
• FORCE MAJEURE - Clause limiting responsibilities of the charterers, shippers and receivers due to events beyond their control.
• FOT - Free On Truck
• FOW (1) - First Open Water
• FOW (2) - Free On Wharf
• FREE OUT - Free of discharge costs to Owners
• FWAD - Fresh Water Departure Draft
• FYG - For Your Guidance
• FYI - For Your Information
• Letter G
• GA - General Average
• GLS - Gearless
• GNCN - Gencon - a standard BIMCO charter party form
• GN (or GR) - Grain (capacity)
• GO - Gas Oil
• GRD - Geared
• GRT - Gross Registered Tonnage
• GSB - Good Safe Berth
• GSP - Good Safe Port
• GTEE - Guarantee .
• Letter H
• 2H - Second Half
• HA - Hatch
• HDWTS - Half Despatch Working Time Saved
• HMS - Heavy Metal Scrap
• HO - Hold
• HW - High Water
• Letter I
• ILOHC - In Lieu of Holds Cleaning
• IMDG - International Maritime Dangerous Goods Code
• IMO - International Maritime Organisation
• IND - Indication
• INTERMODAL - Carriage of a commodity by different modes of transport, i.e. sea, road, rail and air within a single journey.
• ITF - International Transport Federation - international body that regulates crewing of ships
• IU - If Used
• IUATUTC - If Used, Actual Time Used To Count
• IUHATUTC - If Used, Half Actual Time Used To Count
• IWL - Institute Warranty Limits
• Letter L
• LANE METER - A method of measuring the space capacity of Ro/Ro ships whereby each unit of space (Linear Meter) is represented by an area of deck 1.0 meter in length x 2.0 meters in width.
• LASH (1) - To hold goods in position by use of Ropes, Wires, Chains or Straps etc.
• LASH (2) - Lighter Aboard Ship - a vessel that loads small barges direct from the water
• LAT - Latitude
• LOA - Length Overall of the vessel
• LOW - Last Open Water
• LS (or LUMPS) - Lumpsum
• LSD - Lashed Secured Dunnaged
• LT - Liner Terms
• LW - Low Water
• LYCN - Laycan (Layday Cancelling Date)
• Letter M
• MB - Merchant Broker
• MDO (DO) - Marine Diesel Oil
• MIN/MAX - Minimum/Maximum (cargo quantity)
• MOLCHOPT - More or Less Charterers Option
• MOLOO - More or Less Owners Option
• MT - Metric Tonne (i.e. 1,000 kilos / 2204.6lbs)
• M/V - Motor Vessel
• Letter N
• NAABSA - Not Always Afloat But Safely Aground
• NCB - National Cargo Bureau
• NESTING - Implies that cargo is presented stacked in the contour of similarly shaped cargo, it may be likened to a stack of plates.
• NON-REVERSIBLE - (Detention). If loading completed sooner than expected, then saved days will not be added to discharge time allowed.
• NOR - Notice of Readiness
• NRT - Net Registered Tonnage
• NYPE - New York Produce Exchange
• Letter O
• OO - Owners Option
• OSH - Open Shelter Deck
• OWS - Owners
• Letter P
• PASTUS - Past Us
• PC - Period of Charter
• PCGO - Part Cargo
• PCT - Percent
• PDPR - Per Day Pro Rata
• PERDIEM - Per Diem - By the Day
• PHPD - Per Hatch Per Day
• PRATIQUE - License or permission to use a port
• Letter R
• RCVR - Receivers
• REVERSIBLE - (Detention) If loading completed sooner than expected at load port, then days saved can be added to discharge operations.
• ROB - Remaining On Board
• RT - Revenue Tonne (i.e. 1.0 metric Tonne or 1.0 cubic meter, whichever greater). The overall RT is calculated on a line by line basis of the Packing List using the largest amount. The overall freight liability is calculated on the total RT amount, multiplied by the freight rate.
• Letter S
• SATPM - Saturday P.M.
• SB - Safe Berth
• SD (or SID) - Single Decker
• SEAFREIGHT - Costs charged for transporting goods over the sea. This does not cover any haulage or loading/discharging costs but the sea transport only.
• SELFD - Self Discharging
• SF - Stowage factor. Cubic space occupied by one ton (2,240 lbs/1,000 kgs) of cargo.
• SHINC - Sundays/Holidays Included
• SHEX - Sundays/Holidays Excluded
• SKIDS - Are bearers (timber or steel) positioned under cargo to enable fork lift handling at port, and for ease of rigging and lashing on board ship.
• SL - Bale (capacity)
• SOC - Shipper Owned Container
• SOF - Statement Of Facts
• SP - Safe Port
• SRBL - Signing and Releasing Bill of Lading
• SSHEX (or SATSHEX) - Saturdays, Sundays, Holidays Excluded
• SSHINC (or SATSHINC) - Saturdays, Sundays, Holidays Included
• STABILITY - It is paramount that a vessel is stable in all respects at all times. When cargo is loaded/discharged, the stability is monitored by a computer, which takes into account the weight and position of cargo within the vessel.
• STARBOARD - Subject To Enough Merchandise (Availability of Cargo)
• STERN - The aft part of a ship
• SUB - Subject (to)
• SUPERCARGO - Person employed by a ship owner, shipping company, charterer of a ship or shipper of goods to supervise cargo handling operations. Often called a port captain.
• SWAD - Salt Water Arrival Draft
• SWDD - Salt Water Departure Draft
• Letter T
• TBC - to be confirmed
• TC - Time Charter - Owners agree to hire a particular ship for a set length of time
• TEU - Twenty Foot Equivalency Unit - Standard 20‘ Container
• TTL - Total
• TW - Tween Decker
• Letter U
• USC - Unless Sooner Commenced
• UU - Unless Used
• UUIUATUTC - Unless Used If Used Actual Time Used To Count
• Letter V
• VPD - Vessel Pays Dues
• Letter W
• WCCON - Whether Customs Cleared Or Not
• WIBON - Whether In Berth Or Not
• WIFPON - Whether In Free Pratique or not
• WIPON - Whether In Port Or Not
• WLTOHC (distance) - Water Line-To-Hatch Coaming
• WOG - Without Guarantee
• WPD - Weather Permitting Day
• WWD - Weather Working Day
• WRIC - Wire Rods In Coils
• WWR - When, Where Ready
• WWWW - Wibon, Wccon, Wifpon, Wipon
• Letter Y
• YAR - York Antwerp Rules
Siscomex
The Integrated Foreign Trade System - SISCOMEX, established by Decree No. 660 of 09/25/92, is the administrative system of the Brazilian foreign trade, which integrates the related activities of the Bureau of Foreign Trade - SECEX, the Federal Revenue - SRF and the Central Bank of Brazil - Central Bank, on the record, monitor and control the different stages of export operations.
In the design and development of system concepts, codes and classifications have been harmonized, making it possible to adopt a single stream of information handled by computerized road, allowing the elimination of various documents used in processing operations.
Enabling the system
You can have access to SISCOMEX within your own company, if connecting to the system. For this, before the first operation is necessary to address a breakdown of the Federal Revenue in order to get a password. This password is linked to your own CPF.
O acesso ao SISCOMEX pode ser efetuado a partir de qualquer ponto conectado (bancos, corretoras, despachantes aduaneiros ou o próprio estabelecimento do usuário), bem como por meio de terminais instalados nos órgãos federais encarregados do controle do comércio exterior.
Terms of Agreements and blocks
General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
The General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS) is the first multilateral, legally binding set of rules covering international trade in services. The GATS came in January 1995 as part of the OMC. The operation of the GATS are the responsibility of the Council for Trade in Services, consisting of representatives of all OMC countries.
General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT)
The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) has been supplanted as an international organization by the World Trade Organization. An updated General Agreement is now one of the OMC agreements. See "World Trade Organization ', page 15.
North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)
The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) is a comprehensive free trade agreement that are into Canada, Mexico and the United States, established on 1 January 1994 Its objectives include: eliminating barriers to trade in, and facilitate the movement of goods and services across borders; promote conditions of fair competition; increasing investment opportunities; provide adequate and effective protection and enforcement of intellectual property rights; create effective procedures for the implementation and application of the Agreement, for its joint administration and dispute resolution; and establish a base for further trilateral, regional and multilateral. http://www.nafta-sec-alena.org
Free Trade Area of the Americas (ALCA)
The Heads of State and Government of the 34 democracies of the hemisphere at the Summit of the Americas in Miami in 1994, agreed to the creation of a Free Trade Area of the Americas (ALCA), which will be progressively eliminated barriers to trade and investment as well as the conclusion of the negotiations of the Agreement until 2005. http://www.ftaa-alca.org
Latin American Integration Association (ALADI)
The Latin American Integration Association (ALADI) was established by the Treaty of Montevideo in August 1980 and became operational in March 1981 The Association seeks to foster economic cooperation among its members, including through the implementation of regional trade agreements and sectoral agreements. Members (12) include: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Cuba, Ecuador, Mexico, Paraguay, Peru, Uruguay and Venezuela. The ALADI replaced the Latin American Free Trade Association, which was established in 1960 with the goal of developing a common market in Latin America. http://www.aladi.org
Inter-American Development Bank (BID)
Created in 1959, the Inter-American Development Bank (BID) supports economic and social development and regional integration in Latin America and the Caribbean. It does this mainly through lending to public institutions, but also funds private projects, typically in infrastructure and development of capital markets. Members include: Argentina, Austria, Bahamas, Barbados, Belgium, Belize, Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Croatia, Denmark, El Salvador, Ecuador, Slovenia, Spain, USA, Finland, France , Guatemala, Guyana, Haiti, Holland, Honduras, Israel, Italy, Jamaica, Japan, Mexico, Nicaragua, Norway, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Portugal, UK, Dominican Republic, Sweden, Switzerland, Suriname, Trinidad and Tobago, Uruguay and Venezuela. http://www.iadb.org
Trade Capacity Building
Development and improvement of basic skills and capacity of the countries in the area of trade, through technical cooperation and other forms of aid in order to optimize their participation in negotiations, implement their trade commitments, and address the challenges in maximizing the benefits of integration hemispheric. See "Hemispheric Cooperation Program", pagina 15 .
United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL)
Established in December 1966; the United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL) aims to promote the progressive harmonization and unification of international commercial law. Members (36) include: Germany, The Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia, Argentina (alternating annually with Uruguay), Austria, Benin, Brazil, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Canada, China, Singapore, Colombia, Spain, United States, Russian Federation , Fiji, France, Honduras, Hungary, India, Iran, Italy, Japan, Lithuania, Morocco, Mexico, Paraguay, Kenya, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, Romania, Rwanda, Sierra Leone, Sudan, Sweden, Thailand and Uganda. http://www.uncitral.org
United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (CEPAL)
The UN Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (CEPAL) is one of five regional commissions of the United Nations. Was created for the purpose of contributing to the economic development of Latin America, by coordinating actions to this purpose, and strengthen economic relations among countries and with other nations of the world. The promotion of social development of the region was later included among its primary objectives. Its members (41) include: Antigua and Barbuda, Argentina, Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Dominica, El Salvador, Ecuador, Spain, United States, France, Grenada, Guatemala, Guyana, Haiti, Holland, Honduras, Italy, Jamaica, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Portugal, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, Dominican Republic, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Suriname, Trinidad and Tobago, Uruguay and Venezuela; associados- members Anguilla, Aruba, Bonaire, British Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, Puerto Rico and Montserrat. http://www.eclac.org
Trade Negotiations Committee (CNC)
As part of the Free Trade Area of the Americas, the Trade Negotiations Committee (CNC), oversees and manages the process of negotiation of the ALCA vice-ministerial level. The CNC has the responsibility to guide the work of the negotiating groups and special committees of the ALCA and decide on the overall structure of the agreement and institutional issues.
Tripartite Committee
The Tripartite Committee is composed of the Inter-American Development Bank (BID), the Organization of American States (OEA) and the UN Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (CEPAL). It provides analytical, technical and financial support to the ALCA process and maintains the official ALCA website. Each of the institutions of the Tripartite Committee also responds to requests for technical assistance related to ALCA issues, especially the smaller economies of the Hemisphere
Andean Community (CAN)
Once known as the Andean Group (established in 1969) and as the Andean Common Market, the Andean Community (CAN) is a sub-regional organization made up of Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru and Venezuela and the bodies and institutions that form the System Integration Andina. The key objectives of the Andean Community are to promote the balanced and harmonious development of member countries under equitable conditions; stimulate growth through integration and economic and social cooperation; improve participation in the regional integration process with the view to the progressive formation of a Latin American common market; strive for a gradual improvement in the standard of living of its inhabitants. http://www.comunidadandina.org
Community and the Caribbean Common Market (CARICOM)
CARICOM is a group of 15 member countries created by the Treaty of Chaguaramas in 1973 to promote economic integration through free movement of goods and operational cooperation in the areas of education and health. The Treaty was revised in 2001 to make the common market an economic union, the Common Market and the Caribbean Economy (CSME), which provides for the free movement of goods, services, capital and labor-intensive, policy coordination macroeconomic and harmonization of laws and institutions. Members (15) countries are: Antigua and Barbuda, Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Dominica, Grenada, Guyana, Haiti, Jamaica, Montserrat, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Suriname and Trinidad and Tobago. The Bahamas is a member of the Community but not the Common Market. Sound included in associates (3) members: Anguilla, Turk and Caicos Islands and British Virgin Islands. http://www.caricom.org
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)
Founded in December 1964, the UN Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) aims to increase the integration of developing countries into the world economy. UNCTAD is the focal point within the United Nations for the integrated treatment of trade and development and related issues in the areas of finance, technology, investment and sustainable development. Members (191) includes all UN members plus the Holy See. http://www.unctad.org
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)
Founded in November 1989, the Economic Cooperation Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) is the premier forum for facilitating economic growth, cooperation, trade and investment in the Pacific Basin. APEC members (21) are Australia, Brunei, Canada, Chile, China, Singapore, South Korea, United States, Philippines, Hong Kong, Indonesia, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Peru, Russia, Thailand, Taiwan and Vietnam. http://www.apecsec.org.sg
Summit of the Americas
The process of the Summit of the Americas, which began after the first Summit of the Americas in December 1994, brings together the Heads of State and Government of the Western Hemisphere to discuss common concerns, seek solutions and form a shared vision of the future development of the region, economic, social or political. http://www.summit-americas.org
National strategies to strengthen the trade capacity
In the context of the Programme of the ALCA Hemispheric Cooperation, some countries have developed national or regional strategies that define, prioritize, and articulate their needs related to strengthening their ability to: prepare for negotiations; implement trade commitments and adapt to integration. To facilitate coordination and sharing experiences, strategies follow a common format that was developed by the Consultative Group on Smaller Economies, with the help of the Tripartite Committee.
Forum of the Americas Trade and Sustainable Development
Parallel event held by various organizations of civil society with respect to the meeting of the Ministers Responsible for Trade in the Hemisphere participating to the Free Trade Area of the Americas (ALCA).http://www.miami.edu/nsc/pages/FTAA.html
The Americas Business Forum (ABF) - Review Group Summit Implementation (GRIC)
Parallel event held by the private sector with regard to the meeting of the Ministers Responsible for Trade in the Hemisphere participating to the Free Trade Area of the Americas (ALCA). http://www.abfmiami2003.com
Business facilitation measures
The Review Group Summit Implementation (GRIC) was established in March 1995 with the objective of coordinating and implementing the mandates of the Plan of Action Miami. The GRIC consists of 34 democratically elected governments of the hemisphere, which are represented by their National Coordinators appointed. The GRIC is responsible for reporting annually on progress made in meeting the Action Plan to Foreign Ministers. Ministers review the information at the time of the Regular Session of the OEA General Assembly. In the context of the ALCA set of measures adopted by the Ministers Responsible for Trade Ministerial Meeting in Toronto, on November 4, 1999 Delas contains a series of eight measures related to customs and ten measures related to transparency, including, respectively, in Annex II and Annex III of the Ministerial Declaration of Toronto. http://www.ftaa-alca.org/ministerials/minis_e.asp
Central American Common Market (MCCA)
The Central American Common Market was created on December 13, 1960 when Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras and Nicaragua signed the General Treaty on Central American Economic Integration. Costa Rica agreed on July 23, 1962 In October 1993, the five MCCA countries signed the Protocol of Guatemala, which amended the 1960 General Treaty Protocol redefines the objectives, principles and stages of economic integration, and summons members to establish a customs union. More specifically, the Protocol of Guatemala calls members to achieve free trade area of the MCCA through the gradual elimination of tariffs and trade barriers, grant national treatment to intra-regional trade and the adoption of a regional legal framework cobra rules of origin, safeguards, unfair trade practices, intellectual property, services, sanitary and phytosanitary measures, and technical criteria and rules. http://www.sieca.org.gt
Southern Common Market (MERCOSUL)
The Southern Common Market (MERCOSUR) was created by the Treaty of Asuncion on March 26, 1991 Between 1991 and 1995, members of MERCOSUR, Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay, were involved in a series of negotiations to establish a common external tariff, which took place on 1 January 1995 the deadline for the full implementation of the customs union for all members in all sectors is the new 2006 release of the MERCOSUR integration process in 2000 required a coordination closer macroeconomic and other issues of prioritization and the strengthening of institutions, the common external tariff, dispute resolution, remedies to trade and competition policy, and investment incentives. Chile and Bolivia became associate members in, respectively, in 1996 and 1997. http://www.mercosul.org.uy
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OCDE)
The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OCDE) groups 30 member countries in a unique forum to discuss, develop and refine economic and social policies. Was established in December 1960 and came into being in September 1961 members (30) incloem Germany, Australia, Austria, Belgium, Canada, South Korea, Denmark, Slovakia, Spain, United States, Finland, France, Greece, Holland, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, Mexico, Norway, New Zealand, Poland, Portugal, United Kingdom, Czech Republic, Sweden, Switzerland and Turkey. http://www.oecd.org
Organization of American States (OEA)
On April 30, 1948, the Charter of the Organization of American States (OEA) has been adopted by 21 nations of the hemisphere. Affirmed their commitment to common goals and respect for the sovereignty of each nation. Since then, the OEA has expanded to include the nations of the Caribbean and Canada. Through the process of the Summit of the Americas, the Heads of State and Government of the Hemisphere have given important responsibilities and mandates to the OAS, including: human rights; participation of civil society; improve cooperation to address the problem of illegal drugs; support the process to create the Free Trade Area of the Americas; education, justice and security. Members (35) include: Antigua and Barbuda, Argentina, Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba (excluded from formal participation since 1962), Dominica, El Salvador, Ecuador, United States, Grenada, Guatemala, Guyana, Haiti, Honduras, Jamaica, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Dominican Republic, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Suriname, Trinidad and Tobago, Uruguay and Venezuela. http://www.oas.org
World Customs Organization (OMA)
Founded in 1952 as the Customs Co-operation Council, the Council adopted the working name of the World Customs Organization (OMA) in 1994 to more clearly reflect its transition to a truly global intergovernmental institution. The OMA is an independent intergovernmental body whose mission is to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of customs administrations worldwide. With 159 member countries, is the world's only intergovernmental organization with competence in customs matters. http://www.wcoomd.org
World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO)
Created in 1967, the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) is an international organization dedicated to promoting the use and protection of literary, artistic and scientific works. WIPO is one of the 16 specialized agencies of the UN system. It administers 23 international treaties dealing with different aspects of intellectual property protection. The organization has 179 member countries. http://www.wipo.org
World Trade Organization (OMC)
The World Trade Organization succeeded the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) on January 1st 1995 is the only multilateral organization that serves as a forum for negotiating trade liberalization, an entity to oversee the implementation of multilateral trade rules accepted and engaging and a forum for resolving trade disputes. The aim of the WTO is to promote the liberalization and expansion of international trade in goods and services under certain conditions and predictable. The OMC has 146 members. http://www.wto.org
Website ofALCA
Official website of the Free Trade Area of the Americas - http://www.ftaa-alca.org
Hemispheric Cooperation Program (PCH)
The Hemispheric Cooperation Program (PCH) aims to strengthen the capacities of countries seeking assistance to participate in the ALCA negotiations, implement their trade commitments, and address the challenges and maximize the benefits of hemispheric integration, including productive capacity and competitiveness in the region . The program inclói a mechanism to help these countries to develop national and / or regional strategies to enhance capacity building in the area of trade that define, prioritize and articulate their needs and programs that pursue these strategies, and identify sources of financial support and non-finance to meet those needs. The PCH was endorsed by the Ministers Responsible for Trade during the ALCA meeting in Quito in November 2002. http://www.ftaa-alca.org/ministerials/quito/minist_e.asp
Program elimination of tariffs
Schedules of tariff elimination of the Parties to a trade.
ministerial meeting
The regular meeting of Ministers Responsible for Trade of the 34 participating countries in the Free Trade Area of the Americas.
Uruguay Round of Multilateral Trade Negotiations
Initiated in September 1986 in Punta del Este, Uruguay, the eighth round of multilateral trade negotiations agenda covered a broad scope covering many new trade policy issues. The resulting agreement, concluded in December 1993 and signed in April 1994, extended the multilateral trading system into several new areas, notably trade in services and intellectual property rights, and bring important sectors of agriculture and industry textile in multilateral trade rules. The Uruguay Round outcome was the establishment of the World Trade Organization in January 1995. http://www.wto.org/english/thewto_e/whatis_ e/tif_e/fact5_e.htm
Treatment differences in levels of development and size of economies
Principle that provides countries with different levels of development and size the opportunity to get a different treatment in the context of the ALCA negotiations. Principles to this treatment are detailed in the Trade Negotiations Committee document entitled "Principles and Guidelines for the Treatment of Differences in Levels of Development and Size of Economies". http://www.ftaa-alca.org/TNC/tn18e.asp
European Union (UE)
The European Union (EU) consists of fifteen member states through a series of common institutions where decisions on specific matters of joint interest are taken to européio level. It was founded as the European Community after the Second World War to improve the political, economic and social cooperation among its members. The "single market", adopted in 1992 by the Treaty of 12 nationals in EU countries, along with a European Central Bank appeared on 1 January 2002 Member states (15) are Austria, Belgium, Maastricht , is the center of the current European Union. Encompasses freedom of movement for goods, services, people and capital and is grounded by a variety of supportive policies. A common currency, the "Euro", which replaced the old currencies Denmark, Finland, Greece, France, Holland, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Portugal, Sweden and the UK. Ten new member states were invited for ¬se join the EU on May 1, 2004: Cyprus, Slovakia, Slovenia, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Czech Republic. http://europa.eu.int














